A conventional diesel injection system is the heart of every diesel engine, ensuring precise fuel delivery, combustion, and power generation. Understanding how it works can help drivers, engineers, and mechanics maintain efficiency, power, and fuel economy. This article explores the 10 best ways to understand and optimize the performance of your diesel injection system.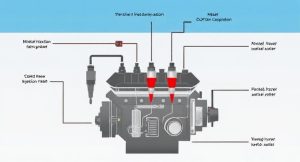
Modern diesel engines depend on controlled fuel atomization and timing to achieve higher torque and lower emissions. By learning how this system functions, you can detect faults earlier and prevent costly breakdowns. In this guide, we’ll break down the science behind diesel injection, its components, and practical ways to enhance its performance.
With proper understanding and maintenance, your diesel vehicle can operate with smoother ignition, stronger combustion, and reduced black smoke. Let’s explore the 10 best ways to understand how a conventional diesel injection system truly works.
How Does A Conventional Diesel Injection System Work?
1. Understanding Fuel Atomization – Best for Complete Combustion Efficiency
Fuel atomization is the process by which diesel fuel is broken down into fine particles for better mixing with air. This is one of the most vital functions of a diesel injection system, as it directly affects combustion quality and engine performance. The smaller the fuel droplets, the more efficiently they burn, leading to cleaner exhaust and more power output.
In a conventional diesel system, injectors spray the fuel at extremely high pressures (up to 1,600 bar or more). This pressure ensures the fuel vaporizes and mixes perfectly with the compressed air in the combustion chamber. Any malfunction in atomization leads to incomplete combustion, loss of power, and increased soot production.
Optimizing atomization through regular maintenance of injectors and filters ensures better mileage and lower carbon emissions. Proper atomization also supports cold-start performance, making the engine more reliable in all weather conditions.
Pros:
• Higher efficiency
• Clean burn
• Less soot
• More torque
• Lower emissions
• Better cold starts
• Improved longevity
Cons:
• High pressure needs
• Costly injectors
• Complex calibration
2. Injector Pump Function – Best for Fuel Delivery Control
The injector pump is the brain of the diesel injection system, managing when and how much fuel reaches each cylinder. It ensures that every combustion stroke receives the right fuel quantity for optimal power generation. Traditional pumps like inline and rotary designs remain the backbone of conventional diesel engines.
A standard inline pump uses plunger-type mechanisms to deliver fuel at extremely high pressures to individual injectors. These pumps are synchronized with the camshaft, ensuring precise fuel timing. Rotary pumps, on the other hand, handle multiple injection points using a rotating distributor head, ideal for smaller engines.
Without an accurate injector pump, your diesel engine could misfire, overheat, or experience reduced fuel economy. Regular inspection and calibration keep the pump functioning efficiently for years.
Pros:
• Precise delivery
• Reliable control
• Durable design
• Easy calibration
• Stable operation
• Compatible with many engines
• Long service life
Cons:
• Requires skill
• Sensitive parts
• Costly repair
3. Injection Timing Adjustment – Best for Engine Power Balance
Injection timing determines when fuel enters the combustion chamber relative to the piston’s position. Correct timing ensures efficient combustion, smooth idling, and maximum power output. In a conventional diesel system, timing is typically controlled mechanically using camshaft synchronization.
If fuel is injected too early, combustion pressure increases and causes knocking. If it’s too late, the fuel may not burn fully, leading to smoke and power loss. Therefore, maintaining accurate timing is essential for fuel economy and engine health.
Modern tuners often use timing lights or digital calibrators to fine-tune the injection phase. A difference of just a few degrees can drastically change torque and fuel use.
Pros:
• Better power
• Lower smoke
• Smooth operation
• Reduced noise
• Optimal burn
• Fuel savings
• Longer engine life
Cons:
• Needs expertise
• Risk of misfire
• Sensitive to wear
4. High-Pressure Fuel Lines – Best for Consistent Pressure Flow
The high-pressure fuel lines transport diesel from the pump to injectors at extremely high pressures. These lines must maintain structural integrity to prevent leaks and maintain consistent pressure. In most diesel systems, pressures range from 1,000 to 2,000 bar, ensuring fuel atomization.
Over time, vibration, corrosion, or improper installation can weaken fuel lines. Any pressure loss can affect injector spray quality and combustion. That’s why proper inspection, torqueing, and replacement are essential for safe operation.
Stainless steel and reinforced synthetic lines are preferred for durability and flexibility. A single leak can reduce performance and create safety hazards.
Pros:
• Consistent pressure
• Long lifespan
• Corrosion-resistant
• Maintains performance
• Improves safety
• Reduces leaks
• Supports atomization
Cons:
• Costly materials
• Hard to replace
• Sensitive to bends
5. Injector Nozzle Design – Best for Precise Spray Pattern
The injector nozzle determines how diesel fuel enters the combustion chamber. Its design defines droplet size, direction, and spray cone angle. The better the nozzle design, the cleaner and more efficient the burn.
Multi-hole nozzles are widely used because they create a fine mist that mixes thoroughly with compressed air. Clogged or worn-out nozzles can lead to poor atomization and excessive smoke. Cleaning or replacing them periodically improves performance and fuel economy.
In advanced systems, nozzle pressure can reach 2,500 bar, enabling ultra-fine atomization for lower emissions. This small component has a massive impact on your engine’s health.
Pros:
• Perfect atomization
• Less smoke
• Better fuel burn
• Easier starts
• Longer lifespan
• Improved torque
• Reduced carbon buildup
Cons:
• Expensive parts
• Prone to clogging
• Needs regular cleaning
6. Governor Mechanism – Best for Speed and Load Control
The governor in a diesel system controls engine speed by regulating the amount of fuel delivered. This ensures stability even when the load changes abruptly. Without a governor, the engine could overspeed or stall during variable conditions.
Mechanical governors are commonly used in conventional diesel engines. They use centrifugal force to adjust the fuel rack position based on RPM. This keeps the engine running at a steady speed and prevents runaway acceleration.
Governors are especially vital for tractors, generators, and heavy vehicles that operate under fluctuating loads. Proper adjustment helps improve throttle response and safety.
Pros:
• Stable RPM
• Safer operation
• Load control
• Prevents damage
• Smooth throttle
• Consistent torque
• Fuel efficiency
Cons:
• Mechanical wear
• Calibration needed
• Limited accuracy
7. Fuel Filters and Water Separators – Best for Clean Diesel Flow
Clean fuel is critical for any diesel injection system. Fuel filters and water separators prevent dirt, rust, and moisture from entering the injectors or pump. Contaminants can destroy high-precision components and reduce fuel efficiency drastically.
A dual-stage filter setup is ideal—one filter removes large particles, and another catches microscopic impurities. Water separators are crucial in humid environments to prevent rust and microbial growth in fuel tanks.
According to recent engine maintenance statistics, up to 85% of injector failures are due to dirty fuel. Regular replacement ensures smooth flow and reduces costly repairs.
Pros:
• Clean fuel
• Protects injectors
• Extends lifespan
• Improves mileage
• Prevents clogging
• Reduces corrosion
• Enhances reliability
Cons:
• Needs replacement
• Adds cost
• Sensitive seals
8. Compression Ratio Optimization – Best for Power and Efficiency
The compression ratio defines how much air is compressed before fuel injection. Diesel engines typically operate at ratios between 16:1 and 22:1, far higher than gasoline engines. This high compression enables spontaneous ignition without spark plugs.
Optimizing the compression ratio enhances combustion efficiency, torque, and thermal performance. Too low a ratio reduces power, while too high increases stress and fuel consumption. Balancing this ratio is key for reliable operation.
Technicians often adjust piston crown shapes or gasket thickness to modify compression levels safely. This ensures perfect ignition conditions for every cycle.
Pros:
• Better power
• Improved torque
• Efficient burn
• Fuel savings
• Reliable starts
• Low emissions
• Enhanced durability
Cons:
• Hard to adjust
• May cause knock
• Increases stress
9. Air Intake and Turbocharging – Best for Improved Combustion
A turbocharger compresses incoming air, increasing oxygen availability for combustion. When combined with a conventional diesel injection system, it dramatically boosts power and fuel efficiency. More air means more energy per stroke.
The turbocharger relies on exhaust gases to spin its turbine, forcing extra air into the cylinders. This creates a powerful feedback loop, improving fuel burn and reducing black smoke. Proper air filtration ensures clean air reaches the turbo and combustion chamber.
Turbocharged diesel engines can deliver up to 30% more power with similar fuel consumption. They also perform better at high altitudes and under heavy loads.
Pros:
• More power
• Better combustion
• Less smoke
• Fuel economy
• Improved torque
• Higher efficiency
• Durable performance
Cons:
• Needs cooling
• Expensive repairs
• Turbo lag
10. Regular System Calibration – Best for Long-Term Performance
Regular calibration ensures that each component of the diesel injection system operates as designed. Over time, wear and tear can alter fuel delivery, timing, and pressure, reducing efficiency. A calibrated system restores power, fuel economy, and smooth operation.
Professional technicians use test benches and flow meters to fine-tune injectors, pumps, and lines. This process verifies uniform fuel delivery to all cylinders. Most experts recommend calibration every 20,000–30,000 miles for optimal performance.
Proper calibration helps avoid hard starts, rough idling, and black exhaust. It’s one of the simplest yet most powerful ways to extend engine life.
Pros:
• Maintains power
• Improves mileage
• Reduces smoke
• Extends life
• Smooth operation
• Reliable starts
• Saves money
Cons:
• Needs tools
• Requires skill
• Time-consuming
How Does A Conventional Diesel Injection System Work (FAQs)
1. What is the main purpose of a diesel injection system?
The main purpose is to deliver diesel fuel at the right time, pressure, and quantity for optimal combustion and power generation.
2. What happens if the diesel injector pump fails?
A faulty pump can cause misfiring, poor fuel economy, and engine stalling due to incorrect fuel pressure or timing.
3. How often should injectors be serviced?
Experts recommend servicing or replacing injectors every 60,000–80,000 miles, depending on fuel quality and maintenance habits.
4. Can water damage a diesel injection system?
Yes, water causes rust, corrosion, and microbial growth, which can damage injectors and pumps permanently.
5. What is the typical injection pressure in diesel systems?
Modern conventional systems operate between 1,000–2,500 bar, ensuring fine atomization and complete combustion.
6. Why is calibration necessary?
Calibration keeps the system in sync, ensuring each cylinder receives the correct fuel amount for balanced performance.
7. What are the signs of a faulty injector?
Common signs include black smoke, rough idling, hard starting, and increased fuel consumption.
Conclusion
Understanding how a conventional diesel injection system works is crucial for anyone who wants to keep their engine efficient, powerful, and clean. Each of the 10 methods above helps improve performance and extends the engine’s lifespan. Regular maintenance, clean fuel, and proper calibration are your best tools for success.
With these principles, you can prevent costly repairs and maintain top-level performance under all conditions. Always consult professionals for adjustments or repairs to avoid internal damage.
Take charge of your diesel engine’s health today—schedule a fuel system inspection, upgrade filters, and monitor injector performance. Your vehicle will reward you with more power, cleaner emissions, and longer life.
Start now — keep your diesel engine performing at its best and experience the smooth, powerful drive you deserve.
Recent Posts
The best houseplants for beginners with a busy schedule make it possible to enjoy greenery at home without constant care. Many people want indoor plants but worry they will not have enough time to...
The best plants for ghost shrimp play a crucial role in creating a healthy and balanced aquarium environment. Choosing the right aquatic plants provides natural shelter, encourages grazing, and helps...